You can get ISRO (Scientist/Engineer 'SC' EC-2010) question paper from internet. I am trying to solve these questions. If there is any wrong in my answers then please reply me. This post contains the following answers
(6)-b, (11)-d, (13)-a, (15)-d, (16)-c, (18)-c, (19)-b, (20)-b, (24)-d, (25)-b, (29)-c, (31)-c, (34)-b, (35)-d, (38)-a, (41)-c, (72)-c, (76)-c, (78)-a, (79)-b
EXPLANATIONS
(6)-b
Note: Design For Testing is a testing process which is done during the manufacturing of different Integrated circuits and hardware. This test is generally done to ensure that the hardware contains no defects that may lead to malfunctioning of the hardware or IC. Application Specific Integrated Circuits (ASIC) are those integrated circuits which are built for a particular purpose.
(11)-d
Note: Stripline is a conductor which is placed inside a dielectric and the dielectric is again sandwiched by two ground plane on opposite side. Microstrip line is a conductor separated from the ground plane by a dielectric. It acts like a transmission line which is fabricated just like the printed circuit board(PCB). The main disadvantage of microstrip line is the unwanted radiation loss. As the microstrip is completely an open structure the radiation loss is more here. One disadvantage of stripline is it is more expensive to manufacture compared to microstrip.
(13)-a
Note:
(15)-d
Note: Rank of a matrix is equal to the order of highest non-zero minor. So the rule is: A matrix 'M' is said to be of rank p if and only if there is at least one minor of the matrix 'M' of order p is not zero and all other minors of matrix 'M' of order p+1 are zero.
(16)-c (I have done it by method of rejection)
Note: 'a' is wrong because the summation of eigen values of a matrix is called trace of the matrix. 'b' is wrong because the eigen values of a skew matrix are purely imaginary and eigen values of symmetrix matrix are real. 'd' is wrong because according to Rouche-Capelli theorem if the rank of augmented matrix is greater than the rank of the coefficient matrix than the system is inconsistent.
(18)-c
(19)-b
Note: GDS-II is a binary file which contains all the information about the layout of a integrated circuit. This file format can be used for reconstructing the entire layout structure of an ICs and also to transfer the layout to a different tool. This is the lowest level of abstraction for the representation of digital system.
(20)-b
Note: MVI - Move Immediate 8-bit data - The immediate 8-bit data will be stored in the destination register. ORA - It will do the logical OR operation of the register with the accumulator and the result will be stored in accumulator. RLC - Rotate accumulator left - Each bit of accumulator will be shifted by one position left. Bit D7 is placed in the position of D0.
A = A7h = 10100111
10100111
-----------
A OR A = 10100111
Now shifting each bit of accumulator by one position left we get 01001111 = 4fh
(24)-d
Note: Schottky diode is a diode whose forward voltage drop lies between 0.15-0.45 volts. This voltage drop is very low as compared to 0.6-1.7 voltage drop of a normal PN junction diode.
As there is no charge carrier in the depletion region its reverse recovery time is very less. Hence it quickly changes its state from conducting to non conducting and vice versa which leads to increased efficiency. The major disadvantage of Schottky diode is its high reverse leakage current.
(25)-b
Note: In UJT relaxation oscillator, frequency of oscillation is
(29)-c
(34)-b
Note: Shannon-Hartley theorem tells a relation between channel capacity(C), bandwidth(B) and signal to noise ratio(S/N).
(35)-d
Note:
(41)-c
(16)-c (I have done it by method of rejection)
Note: 'a' is wrong because the summation of eigen values of a matrix is called trace of the matrix. 'b' is wrong because the eigen values of a skew matrix are purely imaginary and eigen values of symmetrix matrix are real. 'd' is wrong because according to Rouche-Capelli theorem if the rank of augmented matrix is greater than the rank of the coefficient matrix than the system is inconsistent.
(18)-c
Note: The content of the shift register will be changed in the following sequence.
1010-->1101-->0110-->0011-->0001-->1000-->0100-->1010 (here --> represents the clock pulse) (19)-b
Note: GDS-II is a binary file which contains all the information about the layout of a integrated circuit. This file format can be used for reconstructing the entire layout structure of an ICs and also to transfer the layout to a different tool. This is the lowest level of abstraction for the representation of digital system.
(20)-b
Note: MVI - Move Immediate 8-bit data - The immediate 8-bit data will be stored in the destination register. ORA - It will do the logical OR operation of the register with the accumulator and the result will be stored in accumulator. RLC - Rotate accumulator left - Each bit of accumulator will be shifted by one position left. Bit D7 is placed in the position of D0.
A = A7h = 10100111
10100111
-----------
A OR A = 10100111
Now shifting each bit of accumulator by one position left we get 01001111 = 4fh
(24)-d
Note: Schottky diode is a diode whose forward voltage drop lies between 0.15-0.45 volts. This voltage drop is very low as compared to 0.6-1.7 voltage drop of a normal PN junction diode.
 |
| Schottky Diode |
(25)-b
Note: In UJT relaxation oscillator, frequency of oscillation is
(29)-c
Note: Ampere's law defines the force of interaction between two current carrying conductor. According to this law force between two parallel conductors is given by
F is the force between the two conductors. I1,I2 are current flowing through the conductors. l is the length of each conductor. d is the distance between the conductors.
(31)-c
Note:(31)-c
(34)-b
Note: Shannon-Hartley theorem tells a relation between channel capacity(C), bandwidth(B) and signal to noise ratio(S/N).
(35)-d
Note: As we know that
(38)-aNote:
(41)-c
Note: Rowland's law or Hopkinson's law for magnetic circuit is equivalent to Ohm's law in electric circuit. According to Ohm's law E=IR where E is EMF, I is current and R is electric resistance. Similarly according to Rowland's law F=Φℜ where F is magneto-motive force, Φ is magnetic flux and ℜ is magnetic reluctance.
(72)-c
Note:
(76)-c
Note: Zener diode is a diode which allows the current to flow through it in the reverse biased condition when the reverse voltage reaches the break down voltage. Once the break down occurs the voltage remains at the same level irrespective of the power source. This is the reason for which the zener diode is used as the voltage regulator. So relating to our problem, here the voltage across the load will be the same as the break down voltage of the last zener diode parallel to it.
(79)-b
Note: Applying Kirchhoff law to the circuit
I(s)=sV2(s)-V2(0)-sI(s)+I(0), putting all the initial condition zero we will get
V1(s)-I(s)-sI(s)=V2(s) and I(s)=sV2(s)-sI(s)
Now putting the value of I(s) from second equation in the first we get Trasfer function=1/(s+1)
Solutions to rest of the questions will be published very soon. Keep on visiting this blog. Thank you.
(72)-c
Note:
(76)-c
Note: A point is said to be in a jump discontinuity if for that point, limit L- and L+ exist but they are not equal.The same has been described in the following graph.
(78)-aNote: Zener diode is a diode which allows the current to flow through it in the reverse biased condition when the reverse voltage reaches the break down voltage. Once the break down occurs the voltage remains at the same level irrespective of the power source. This is the reason for which the zener diode is used as the voltage regulator. So relating to our problem, here the voltage across the load will be the same as the break down voltage of the last zener diode parallel to it.
(79)-b
Note: Applying Kirchhoff law to the circuit
I(s)=sV2(s)-V2(0)-sI(s)+I(0), putting all the initial condition zero we will get
V1(s)-I(s)-sI(s)=V2(s) and I(s)=sV2(s)-sI(s)
Now putting the value of I(s) from second equation in the first we get Trasfer function=1/(s+1)
Solutions to rest of the questions will be published very soon. Keep on visiting this blog. Thank you.



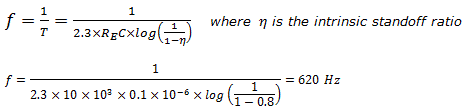








2 comments:
for question 78 made easy gives solution as 9.47v explaining it as 20v zener diode is on and 10v diode is off and hence by applying voltage division rule we will get 9.47v
Kindly comment on it
It's amazing in support of me to have a site, which is beneficial
in support of my knowledge. thanks admin
Post a Comment