- Fan-in
- Fan-out
- Noise margin
- Propagation delay
- Power dissipation
Fan-in
It indicates the number of inputs of an electronic logic gates. For instance a AND gate with 3 inputs has fan-in of 3. But logic gates with higher fan-in tends to be slower.
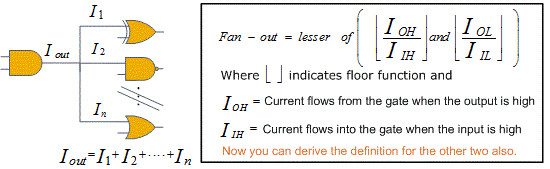
Fan-out
It is the maximum number of inputs that can be driven by the output of another gate. It is generally found that in an integrated circuit the output of a particular gate is connected to input of many other gates.
There is a limit to how many gates a single gate can drive. So maximum fan-out condition indicates that greatest number of inputs that can be safely connected to the output of a gate. A fan-out of 7 means that 7 unit loads can be driven by the single output of the gate with out affecting the output voltage specification.
Description: Lets consider there are two digital circuit A(driving circuit) and B(receiving circuit). Circuit A has been designed to swing between 0V and 2.2 V. But the voltage above 1.9V is considered as logic high and the voltage below 0.2 V is considered as logic low. So for circuit A, VOH=1.9V and VOL=0.2V. Similarly as circuit B is a receiving circuit, the input voltage above 1.6V is logic high and below 0.4 V is logic low. That means for circuit B, VIH=1.6V and VIL=0.4V.
When output voltage of circuit A is low, i.e VO, the input voltage VI must also be low. But because of noise the voltage VI may not be same as VO. It may become higher than that. As long as the increased voltage level is less than VIH, circuit B takes it as a logic low. But if it is more than VIL, it will be implemented as logic high.
Hence there are two different types of noise margin, one for logic high and one for logic zero.
There is a limit to how many gates a single gate can drive. So maximum fan-out condition indicates that greatest number of inputs that can be safely connected to the output of a gate. A fan-out of 7 means that 7 unit loads can be driven by the single output of the gate with out affecting the output voltage specification.
Noise margin
It can be defined as the amount of noise that a circuit can with stand.When output voltage of circuit A is low, i.e VO, the input voltage VI must also be low. But because of noise the voltage VI may not be same as VO. It may become higher than that. As long as the increased voltage level is less than VIH, circuit B takes it as a logic low. But if it is more than VIL, it will be implemented as logic high.
Hence there are two different types of noise margin, one for logic high and one for logic zero.
VNH: Noise margin for logic high[1]=VOH-VIH
VNL:Noise margin for logic low[0]=VIL-VOL
Propagation Delay
When an input changes in a logic gate, output doesn't change instantaneously. Hence the time required for the input to be reflected in the output is called propagation delay.
tPHL= Delay time in going from logic 1 to logic 0.
tPLH= Delay time in going from logic 0 to logic 1.
Power Dissipation
Power dissipation is the amount of energy radiated from the IC in the form of heat.


No comments:
Post a Comment